Types And Classification Of Database Management System
Types And Classification Of Database Management System + PDF – As we all know DBMS is an interesting subject and so is its classification. There are several criteria based on which DBMS is classified. The classification and types of Database Management System(DBMS) is explained in a detailed manner below based on the different factors. At the end of this article, you will be given a free pdf copy of all these types of DBMS.
Types And Classification Of Database Management System + PDF
Based on the data model
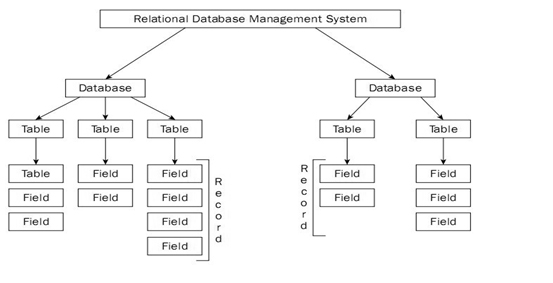
Relational database – This is the most popular data model used in industries. It is based on the SQL. They are table oriented which means data is stored in different access control tables, each has the key field whose task is to identify each row. The tables or the files with the data are called as relations that help in designating the row or record, and columns are referred to attributes or fields. Few examples are MYSQL(Oracle, open source), Oracle database (Oracle), Microsoft SQL server(Microsoft) and DB2(IBM).
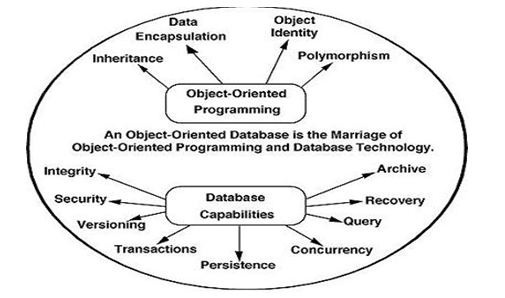
Object oriented database – The information here is in the form of the object as used in object oriented programming. It adds the database functionality to object programming languages. It requires less code, use more natural data and also code bases are easy to maintain. Examples are ObjectDB (ObjectDB software).
Object relational database – Relational DBMS are evolving continuously and they have been incorporating many concepts developed in object database leading to a new class called extended relational database or object relational database.
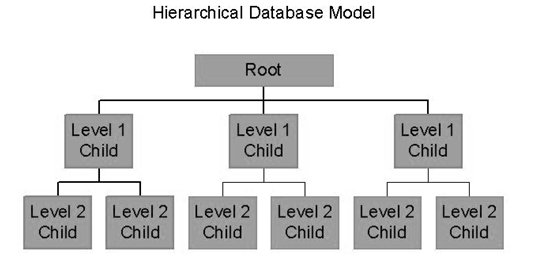
Hierarchical database – In this, the information about the groups of parent or child relationships is present in the records which is similar to the structure of a tree. Here the data follows a series of records, set of values attached to it. They are used in industry on mainframe platforms. Examples are IMS(IBM), Windows registry(Microsoft).
Network database – Mainly used on a large digital computers. If there are more connections, then this database is efficient. They are similar to hierarchical database, they look like a cobweb or interconnected network of records. Examples are CA-IDMS(COMPUTER associates), IMAGE(HP).
Based on the number of users
Single user – As the name itself indicates it can support only one user at a time. It is mostly used with the personal computer on which the data resides accessible to a single person. The user may design, maintain and write the database programs.
Multiple users – It supports multiple users concurrently. Data can be both integrated and shared,a database should be integrated when the same information is not need be recorded in two places. For example a student in the college should have the database containing his information. It must be accessible to all the departments related to him. For example the library department and the fee section department should have information about student’s database. So in such case, we can integrate and even though database resides in only one place both the departments will have the access to it.
Based on the sites over which network is distributed
Centralized database system – The DBMS and database are stored at the single site that is used by several other systems too. We can simply say that data here is maintained on the centralized server.
Parallel network database system – This system has the advantage of improving processing input and output speeds. Majorly used in the applications that have query to larger database. It holds the multiple central processing units and data storage disks in parallel.
Distributed database system – In this data and the DBMS software are distributed over several sites but connected to the single computer.
Further they are classified as
1.Homogeneous DBMS – They use same software but from the multiple sites. Data exchange between the sites can be handled easily. For example, library information systems by the same vendor ,such as Geac Computer corporation, use the same DBMS software that allows the exchanges between various Geac library sites.
2.heterogeneous DBMS – They use different DBMS software for different sites but there is a additional software that helps the exchange of the data between the sites.
Client-server database system – This system has two logical components namely client and server. Clients are generally the personal computers or workstations whereas servers are the large workstations, mini range computers or a main frame computer system. The applications and tools of the DBMS run on the client platforms and the DBMS software on the server. Both server and client computers are connected over the network. We can relate it to client and server in real life to understand in a much better way. Here the applications and tools act as a client send the requests for its services. The DBMS processes these requests and returns the result to the client. Server handles jobs that are common to many clients say database access and updates.
Multi-tier client-server database system – The rise of personal computers in business has increased the reliability of the network hardware leading to evolution of two-tier and three-tier systems which use different software for the client and software.
Based on the cost
Low cost DBMS – The cost of these systems vary from $100 to $3000.
Medium cost DBMS – Cost varies from $10000 to $100000.
High cost DBMS – Cost pf these systems are usually more than $100000.
Based on the access
This classification simply based on the access to data in the database systems
Sequential access – One after the other.
Direct access
Inverted file structures
Based on the usage
Online transaction processing(OLTP) DBMS – They manage the operational data. Database server must be able to process lots of simple transactions per unit of time. Transactions are initiated in real time, in simultaneous by lots of user and applications hence it must have high volume of short, simple queries.
Online analytical processing(OLAP) DBMS – They use the operational data for tactical and strategical decision making. They have limited users deal with huge amount of data,complex queries.
Big data and analytics DBMS – To cope with big data new database technologies have been introduced. One such is NoSQL (not only SQL) which abandons the well known relational database scheme.
XML DBMS – two types
- Native XML DBMS – Use the logical,intrinsic structure of XML document.
2.Enabled XML DBMS – Existing DBMS with facilities to store XML data and structured data in integrated way.
Multimedia DBMS – Stores data such as text, images, audio, video and 3D games which are usually stored in binary large object.
GIS DBMS – Stores and queries the spatial data.
Sensor DBMS – Allows to manage sensor data, bio-metric and telematics data.
Mobile DBMS – Runs on the smartphones, tablets. It Handles the local queries. Supports self management( no DBA).
Open source DBMS – Code is publicly available and can be extended by anyone, popular for small business applications.
As we said that we will provide you a free pdf file of Types and Classification of DBMS, so link to download this pdf file is given below.
Types and Classification of DBMS PDF File
So it was all about types and classification of Database Management System.


I pleased to learn greatly from your DBMS blog, How ever like Oliver Twist, I will be great if you can let me have material on planimetric, altimetric, and plan I metrical time trip classes of database
Thanks sir.classification of DBMS is mostly useful and it is very easily i understand and very helpful for me. Thanks a lot
Sir show the last point based on purpose please with easy way
I found it helpful, thank you. I can now describe the classification of DBMS